Plastic Water Tanks
Introduction
Included in this article is information regarding plastic water tanks and their use.
You will learn more about topics such as:
- What is a Plastic Water Tank
- How Plastic Water Tanks are Made
- Types of Plastic Water Tanks
- Uses for Plastic Water Tanks
- Plastics Used to Make Plastic Water Tanks
- And Much More ...

Chapter One – What is a Plastic Water Tank?
A plastic water tank is a large capacity container designed to store water for household, agricultural, irrigation, and industrial manufacturing use. There are various types of water tanks produced to meet the needs of specific applications, with specialized ones made to adhere to unusual requirements and standards. The term plastic water tank is a generic description of an assortment of plastic tanks purposed to store water. The types of plastics used to produce plastic water tanks are chemically designed for that purpose and meet the standards established by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Of the many types of plastics for plastic water tank construction, polypropylene and polyethylene are the most common.

When choosing a plastic water tank, it is essential to make the selection based on how the tank will be used since different plastic materials are ideal for use with different forms of water. The most rigid restrictions regarding plastic water tanks relate to ones being used to store drinking or cooking water. For those purposes, plastic water tanks must comply with the regulations of the FDA.
The varieties of plastic water tanks range from ones that can be carried and placed in a truck to ones that can hold thousands of gallons of water and be buried. Essentially, there is a plastic water tank for every application and function. The many types and kinds make it possible for plastic water tanks to be able to fit any purpose.
Chapter Two – How Plastic Water Tanks are Made
There are several methods used to make plastic bottles and containers. The sizes of plastic water tanks limit the number of methods available to produce them, including blow molding or rotational molding. Prior to beginning the molding process, manufacturers choose the appropriate polymer to fit the requirements of the proposed plastic water tank, a choice that is critical to the tank’s performance and use.
There are several necessary factors that are considered when shaping a plastic water tank, which include the thickness of the plastic and the desired shape. In the manufacturing process, it is impossible to cut corners or eliminate parts of the process since each step is required to produce a viable and satisfactory product.
Plastic Water Tank Manufacturing
Prior to beginning the production process, manufacturers choose the right polymer for producing a plastic water tank. The polymers that are used the most are polyethylene and polypropylene.
Polyethylene, also known as polythene or polyethene, has a linear structure with ethene being its primary element, which is a stable molecule. During polymerization, a catalyst is added to convert ethylene into polyethylene.

Polypropylene is made from propylene, an organic hydrocarbon, and has physical properties similar to polyethylene. The difference between the polymers is polypropylene’s resistance to heat and its hardness. Polypropylene is more flexible and is resistant to some acids and alkalis.

Rotational Molding
Rotational molding is a fabrication method for the production of hollow parts by placing them in a hollow mold. Once the powder resin is placed in the mold, the mold is rotated.
Rotational Molding Step one
The first step in the rotational molding process is to load the plastic powder polymer into the mold chamber. The amount of polymer determines the size of the plastic water tank and the thickness of its walls. A release agent is coated on the walls of the mold to make the removal of the molded plastic water tank easier.
There is some confusion regarding the description of rotational molding being seamless since there is a line that goes completely around the mold. Rotation molds have a top and bottom that are joined prior to its coating and the loading of the polymer powder. When the top and bottom are bolted together, there is a small offset between the halves that is visible when the finished product is ejected. Regardless of the perceived seam, all rotational mold plastic water tanks are a single leak proof piece.

Molding Step Two
The coated mold with its powdered polymer is placed in a large oven where they are heated to slowly melt the polymer powder. As heat is applied, the mold is rotated in a multi axis way forcing the melted plastic to the sides of the mold.
The diagram below shows the heating process of the mold as it rotates.
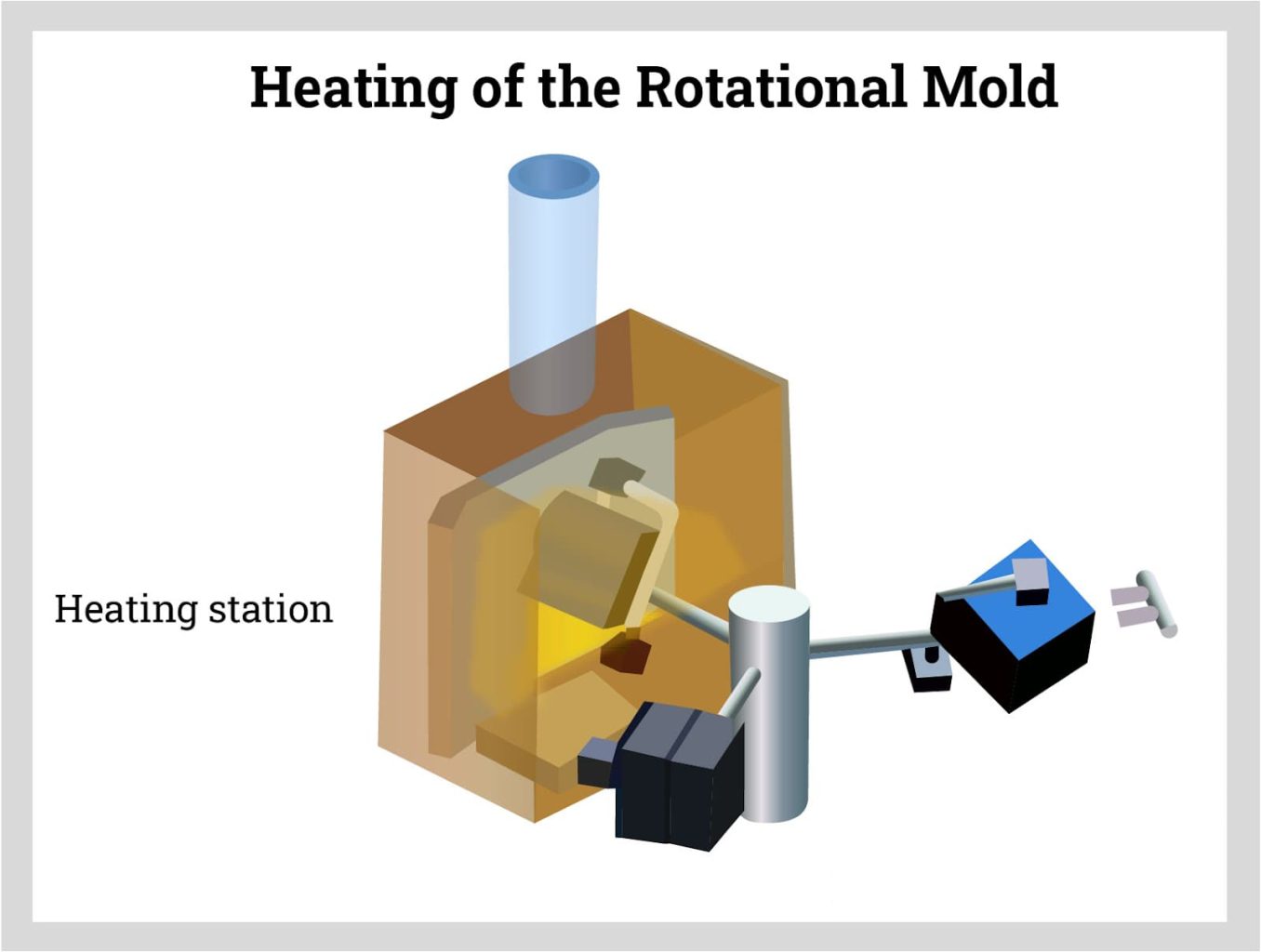
Step Three of Rotational Molding
As the mold is being heated, the mold rotates to distribute the melted polymer across the surface of the mold. The efficiency of the process evenly disperses the material such that it reaches the required thickness for the container and shapes and defines it.
Step Four of Rotational Molding
After a set amount of time, the mold is removed from the heating rotation and placed in a cooling rotation. The cooling process solidifies the plastic against the inside of the mold, a process that takes less than an hour. Cooling is maintained in a specific range to avoid warping and ensure a smooth even finish. The lowered temperature must reach a point where the material is completely solidified, and the completed plastic water tank is safe to handle.
In the image below, the green circle represents the completed plastic water tank that is being subjected to the cooling stage.
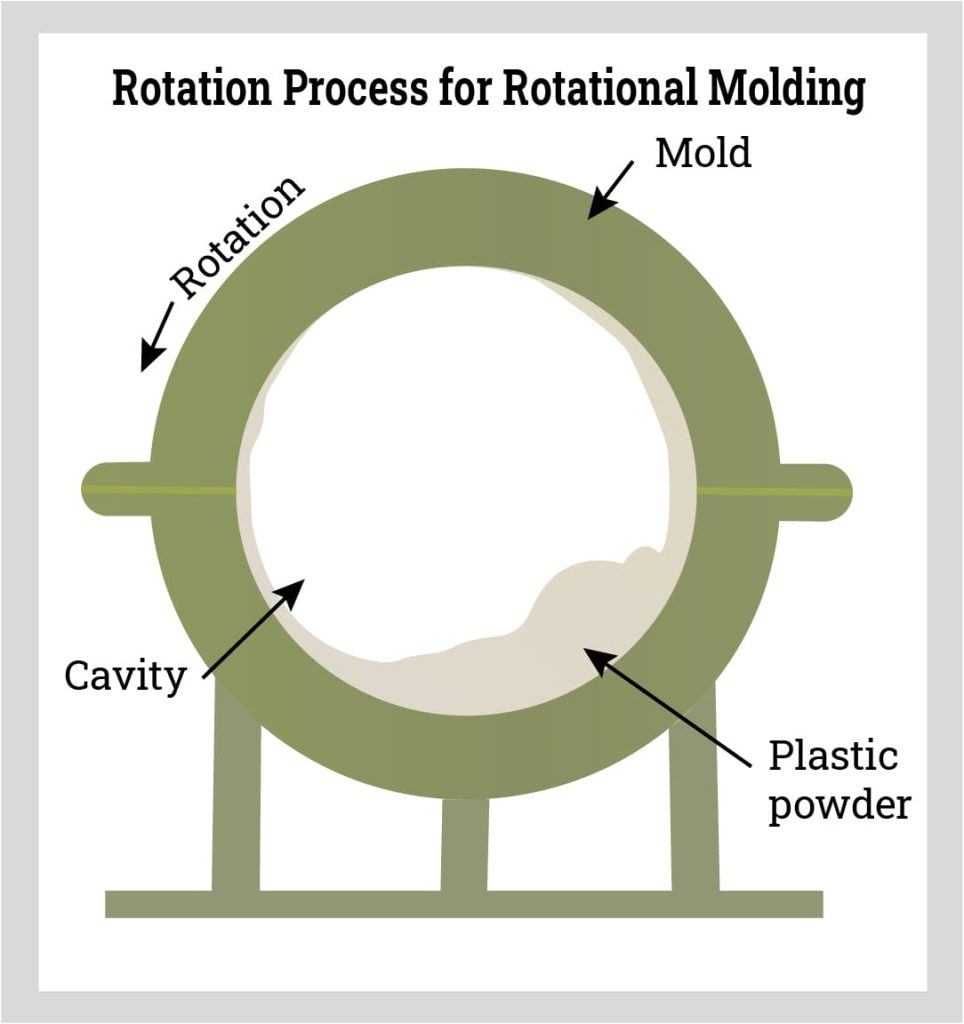
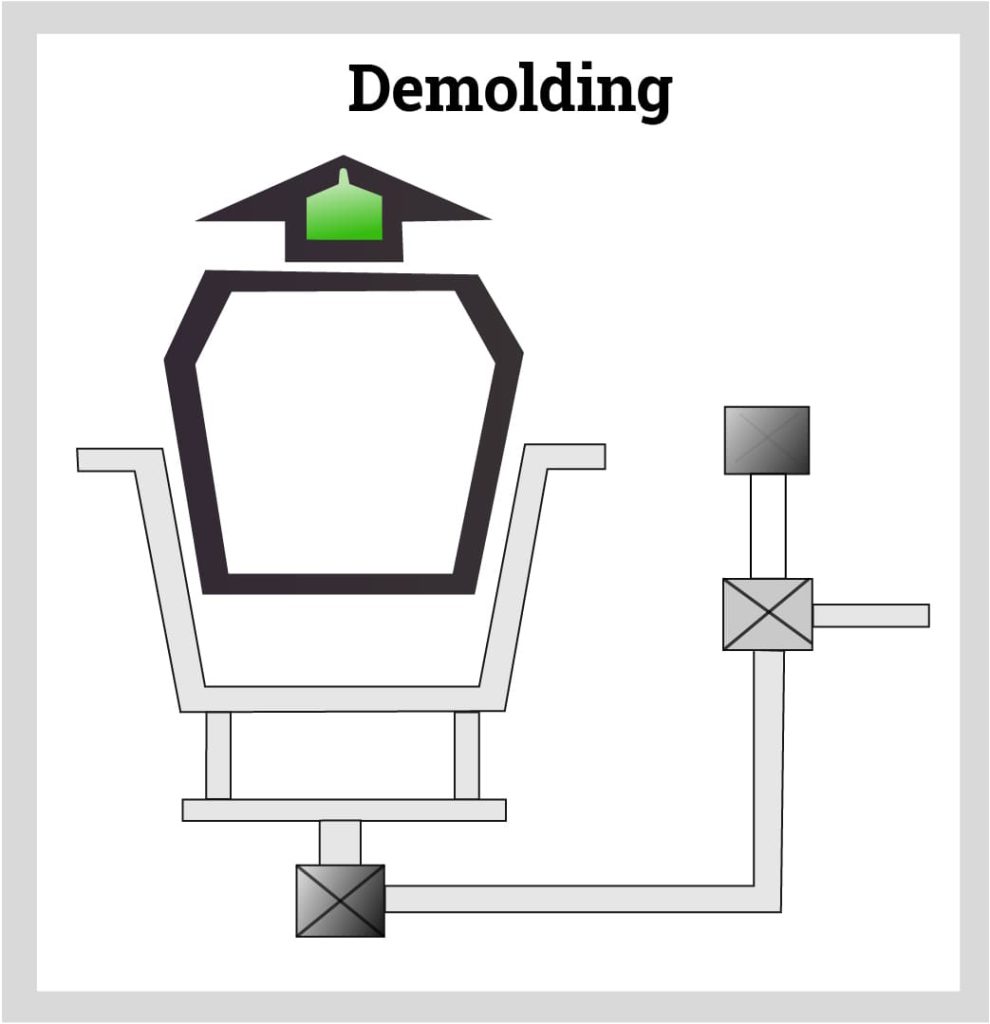
Rotational Molding Step Five
The final step in the rotational molding process is to demold the finished product. Smaller compact plastic water tanks can be easily removed by hand, while larger bulkier ones are removed by a forklift or ejection equipment. A completed plastic water tank is one solid hollow plastic tank that is ready for attaching pipes, fittings, and other assembly components.
Blow Molding
Blow molding has two processes for the production of plastic water tanks, which are injection and extrusion. As with rotational molding, blow molding uses a mold for shaping and creating plastic water tanks. How the molten plastic polymer is inserted into the mold is the difference between the two methods.
Blow Molding Step One
There are two initial steps that are performed before beginning the blow molding process for injection and extrusion blow molding. For the extrusion process, a parison, a tube of molten plastic, is formed to begin the process. For injection molding, a preform is made.
Step Two of Blow Molding
With extrusion blow molding, the parison, that has come from the extruder, is inflated into the mold that conforms to the shape of the plastic water tank.
For injection molding, the preform is created in an injection mold that is shaped by a core rod that is inside the preform and is shaped like the top of the plastic water tank much like a bottle neck. The preform is attached to a core rod with all of the polymer to shape the plastic water tank.
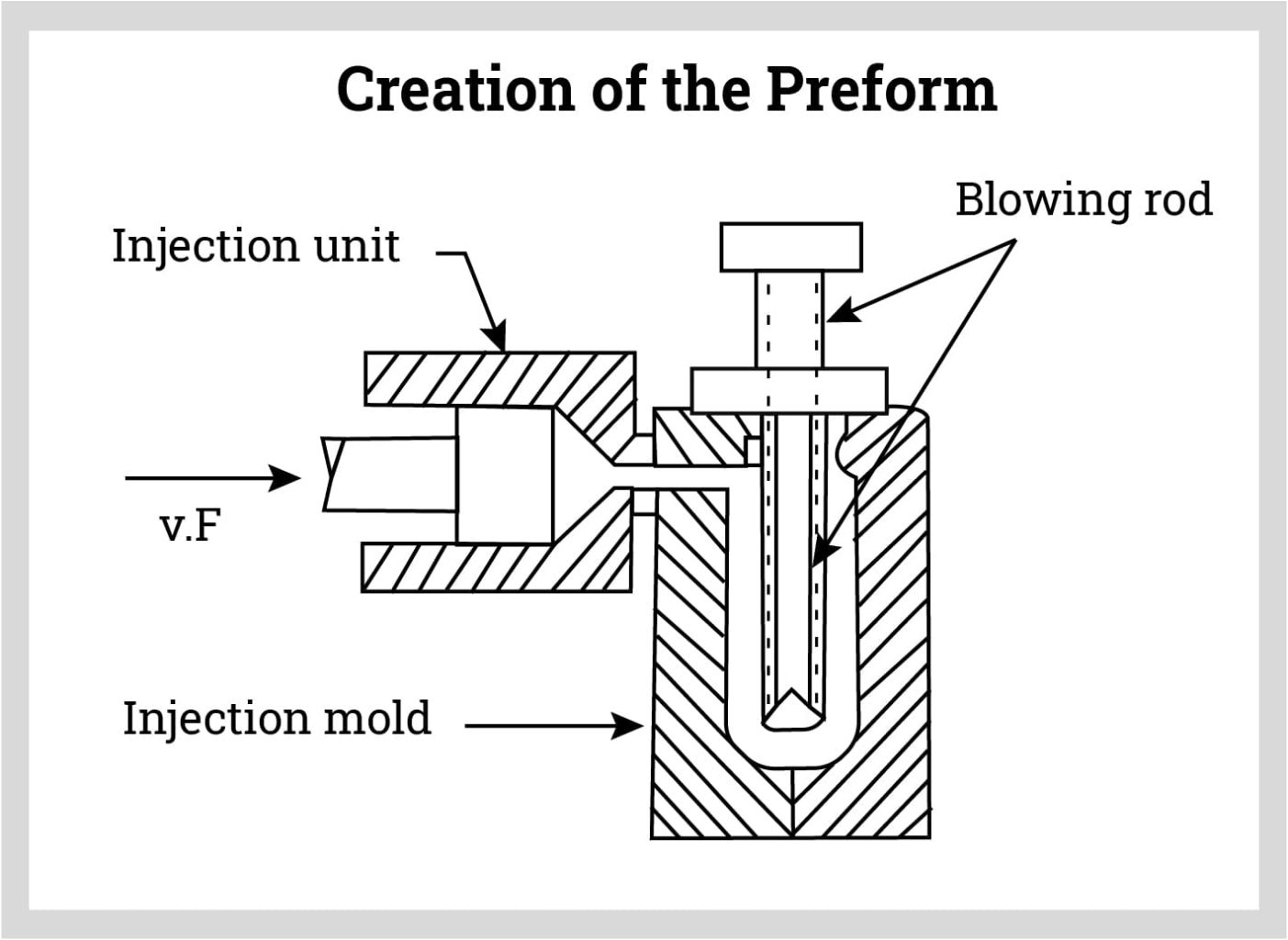
Blow Molding Step Three
In the next step of the extrusion blow molding process, the parison is filled with hot air that forces it to take the shape of the mold cavity.
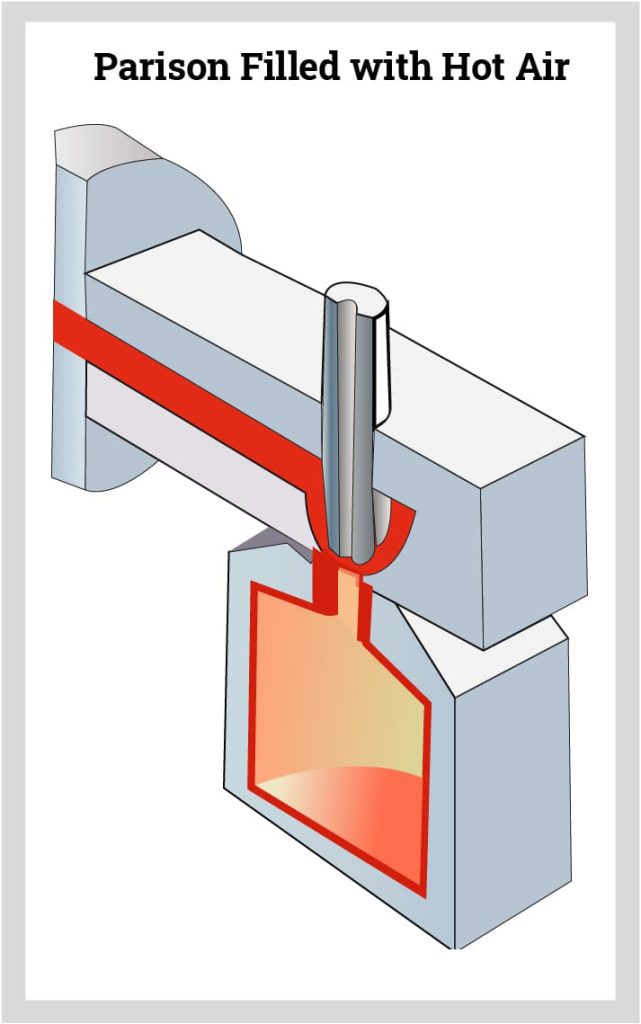
The next step of the injection process is to move the preform from the injection mold to the mold for the plastic water tank. The preform is inflated by an air valve that forces the preform to the sides of the plastic water tank to take its form.
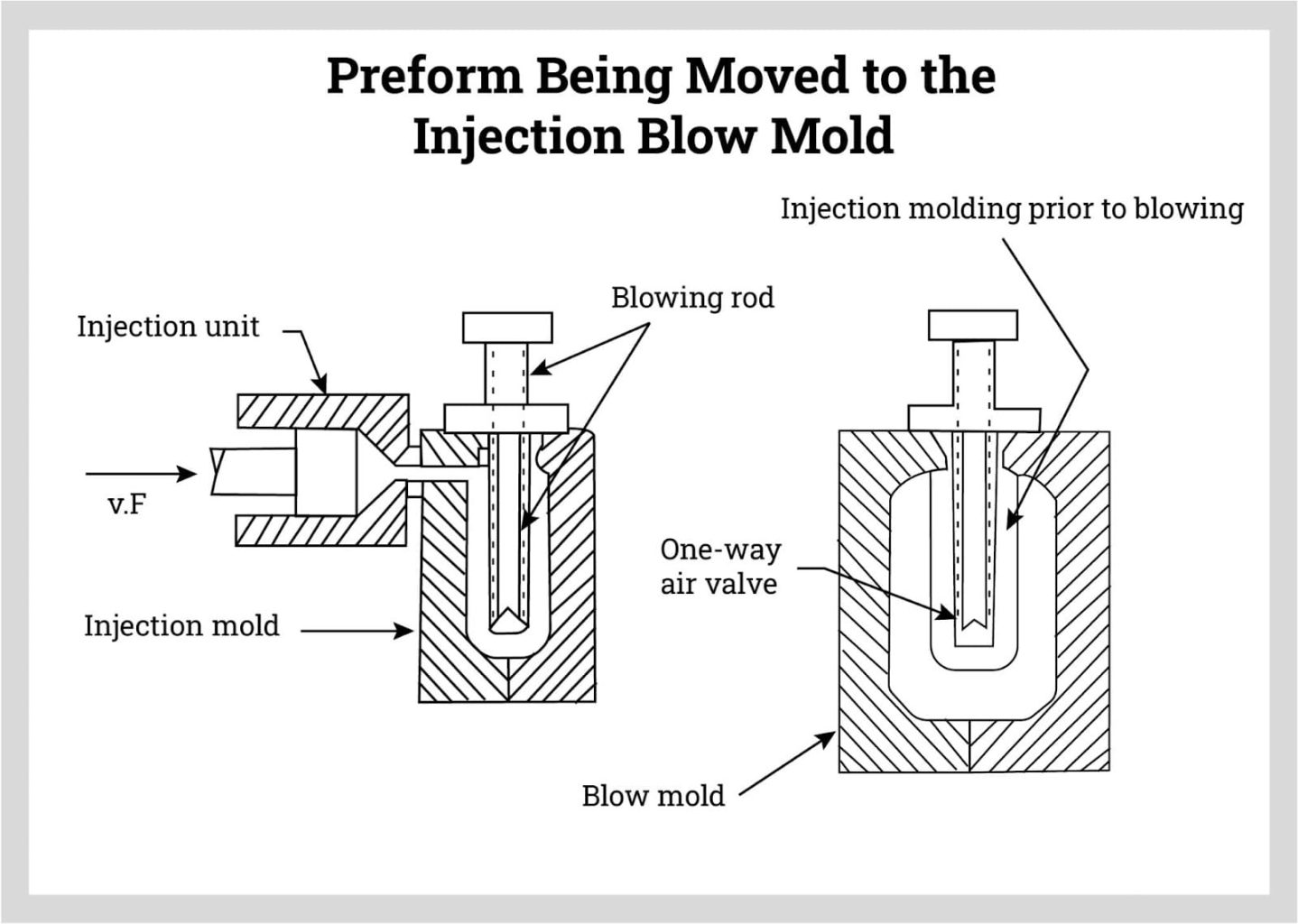
Step Four of Blow Molding
The final step for both processes is to cool the mold and plastic water tank. Once the mold reaches room temperature, its halves are separated, and the completed plastic water tank is removed.
Both forms of blow molding have the ability to produce plastic water tanks with intricate and precise details, although they are best known for the mass production of other plastic products such as soda bottles and other hollow plastic items.
Complete Process for Blow Molding a Plastic Water Tank
The image below provides a picture of a few of the steps used in blow molding a plastic water tank.
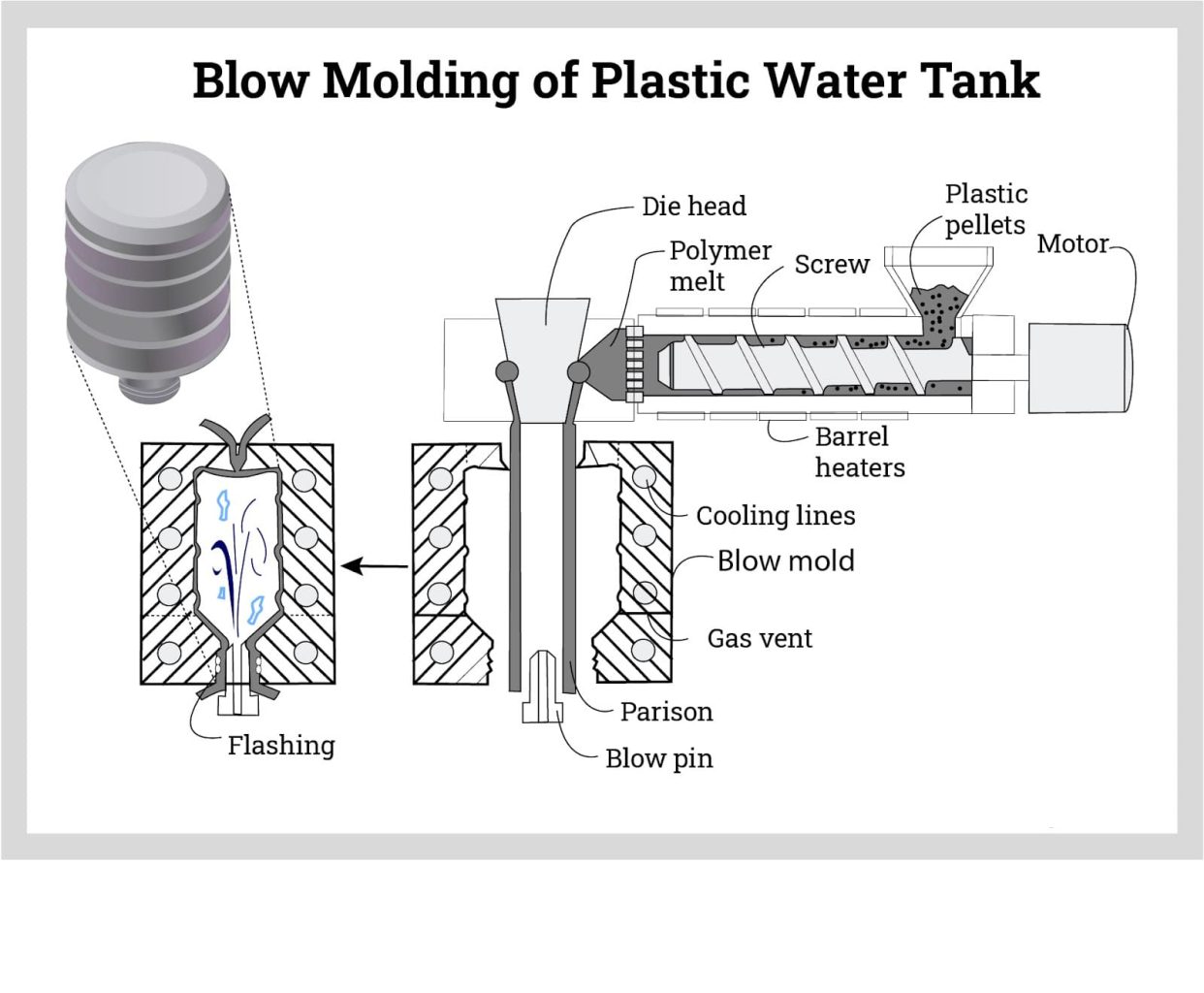
Leading Manufacturers and Suppliers
Chapter Three – Types of Plastic Water Tanks
Plastics are used to manufacture water tanks because of their flexibility to be produced in different sizes with a wide variety of components, additions, and types of materials to fit the type of water. In the simplest terms, water tanks are used to store water for later use. The specific design of tanks is to meet the needs of the water to be stored in them.
A plastic water tank’s size and design requirements determine if the tank can be used for commercial purposes, storing household water, agricultural purposes, irrigation, or manufacturing. Plastic water tanks can also be used for reverse osmosis systems.
Plastic Water Tank Types
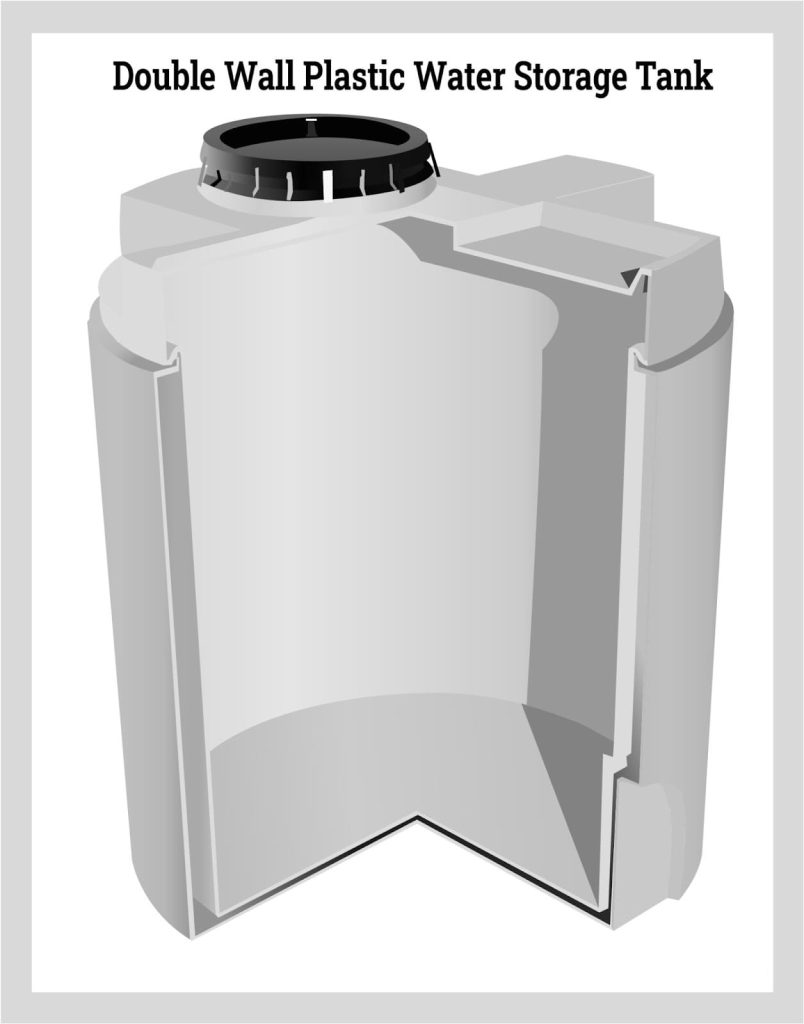
Double Wall Plastic Tank
The unique design of double wall plastic water tanks includes a wall in wall construction with an inner tank and secondary outer tank. The configuration of the wall in the wall plastic tank provides secondary containment of the contents of the tank. They are ideal for environmental safety in regard to water that needs to be contained to prevent pollution. As with all plastic water tanks, wall in wall or double wall plastic tanks come in a wide variety of shapes and sizes.

Elliptical Cradle Plastic Water Tank
Elliptical cradle plastic water tanks lower the center of gravity of the tank, which enhances the tanks stability and visibility during transport. The shape of elliptical plastic water tanks necessitates that their bottom be fully supported by a cradle. They have translucent walls for leveling views and gallon indicators. Though they are designed for water transport, they can also hold fertilizers and compatible chemicals.

Horizontal Plastic Water Tanks
Horizontal plastic water tanks are an above ground water storage tank similar to vertical plastic water tanks. Unlike vertical tanks, they have legs molded into their structure or disconnected ones that they can set on. They are made from polyethylene, high density (HDPE), or cross linked (XLPE).

Open Top Plastic Water Tanks
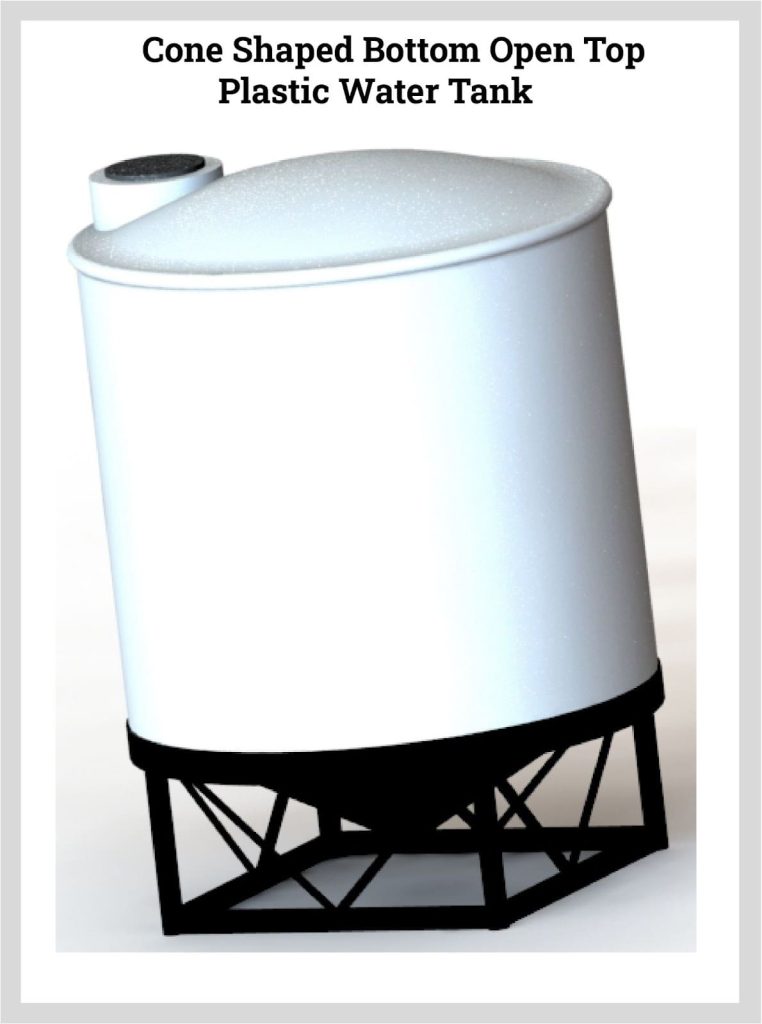
Open top plastic water tanks are used for collection systems or secondary containment for vertical plastic water tanks. In the majority of cases, open top plastic water tanks have tight fitting tops and are made of HDPE or XLPE. Aside from their use for water collection and storage, open top plastic water tanks are used as dipping, chroming, batch, and mixing tanks. They are commonly found in industrial and manufacturing environments.
A special variety of open top plastic water tanks are ones with a cone shaped bottom. The cone shape makes it possible to easily drain and empty the tank. They may have translucent walls for easy viewing of the level of the contents with gallon indicators.

Rectangular Plastic Water Tanks
The shape of rectangular plastic water tanks makes it possible to install and store them in several positions and locations. They are made from LLDPE or low density polyethylene with UV inhibitors to meet the standards for use with food and beverages.
They can come with translucent walls to allow monitoring of the contents of the tank. As with all plastic water tanks, rectangular plastic water tanks have a single unit design without seams or joints.

Stackable Plastic Tanks
Stackable plastic water tanks are designed for use where there is limited space. The freestanding design of stackable plastic water tanks is what makes it possible to place them on top of one another. Like horizontal tanks, stackable plastic water tanks have exceptionally sturdy legs built into their structure. Stackable plastic water tanks come in sizes that range from 30 gallons to over 300 gallons. In most cases, they have tote leg stands for safety and support.

Underground Water Tanks
Underground plastic water tanks are designed to store bulk water or potable water and for underground installation. They are made from UV stabilized polyethylene, a food grade polymer, with ribbing to enhance their durability. Their capacity varies from 260 gallons to over 2000 gallons.

Vertical Plastic Water Tanks
Vertical plastic water tanks are designed to store water above ground and come in green or black to limit the influence of sunlight. They are used to collect rainwater, provide an emergency water supply, farm irrigation, and fire protection.
Chapter Four – Uses for Plastic Water Tanks
There are an endless number of uses for plastic water tanks, aside from their basic purpose for storing water. The wide varieties of uses are due to the adaptability and flexibility of plastic water tanks, which can be configured, shaped, designed, and engineered to perform an assortment of functions.
The factors that make plastic water tanks so adjustable are the materials used to manufacture them, which can be mixed, blended, and chemically altered to enhance their endurance and capabilities.
Plastic Water Tank Usage
Reverse Osmosis
Reverse osmosis is a water purification process that takes a long time and requires a storage tank to hold the water after processing. Plastic water tanks are ideal for the process since they are durable, flexible, and easy to install. They can be located in any position to meet the needs of the process.

Cistern Plastic Water Storage Tanks
A cistern is an underground plastic water storage tank used to safely store potable water. They normally have a capacity of several thousand gallons for agricultural use and hundreds of gallons for residential use. Cistern plastic water storage tanks have ribbed sides for extra support. They are never fully drained in order to prevent the tank from being warped by the surrounding soil.

Doorway Plastic Water Tanks
Doorway plastic water tanks are freestanding tanks that are used for water storage when there is limited space. They are designed to be stored in conventional doorways without the need for supports, legs, or bands. They are made of polyethylene and meet FDA standards. The seamless design prevents cracking or punctures and makes them weather resistant.

Truck Bed Tanks
Truck bed plastic water tanks are specially designed to fit in the bed of a truck with accommodations for wheel wells. As with any water tank for transporting potable water, truck bed plastic water tanks are designed to meet FDA standards. They can come with translucent walls and gallon indicators.

Rainwater Tanks
Plastic rainwater tanks are normally found in urban areas and serve as the main water source. They are made by rotational or injection blow molding in sizes that vary from a few hundred gallons up to over 10,000 gallons. Plastic rainwater tanks have been gradually replacing traditional galvanized steel tanks for several years since they cost less and last longer.
The seamless construction of plastic water tanks makes them invulnerable to cracks, punctures, or leaks. They have exceptional impact strength and resistance to corrosion or rust. Plastic rainwater tanks have a long life span and are easy to install and handle.

Using a Forklift
Plastic water tanks that are designed to be lifted by a forklift are made for light duty water transport. Their base is designed to accommodate forklift forks and have a rectangular metal frame for extra support. Vertical forklift plastic water tanks have a poly base with space for forklift forks. In some designs, their walls are translucent and have gallon markers.
Marine Plastic Water Tanks
The purpose of marine plastic water tanks is to store fresh potable water on boats. They are designed to endure potentially rugged conditions found on sea going vessels.
Like all forms of plastic water tanks, marine water tanks can be installed in any boat regardless of its size.
The long life span of marine water plastic tanks is a feature that boat owners desire the most and the reason marine water plastic tanks are so popular. There is a wide range of sizes from ones that are a few gallons up to ones that are several hundred gallons.

Septic Plastic Tanks
Waste water septic plastic tanks have multiple uses in a variety of conditions, from recreational vehicles and boats to underground tanks for homes and offices. A significant aspect of septic tanks is their capacity, ranging from a few gallons for small sites to over 1000 gallons for large operations.
The unique nature of septic tanks requires that they be specially designed for their purpose and not used for any other application. The polyethylene resins used to make plastic septic tanks prevent cracks and punctures. They are less expensive to purchase and install. For added convenience, dual and double compartment versions of plastic septic tanks are available to decrease the number of times the septic tank needs to be emptied.

The eight uses for plastic water tanks listed above are a small fraction of the many ways that plastic water tanks are utilized. They are exceptionally versatile and are being used in applications that require durable, long lasting, and resilient performance.
Chapter Five – Plastics Used to Make Plastic Water Tanks
There are two polymers that are used to produce most plastic water tanks: polypropylene and polyethylene. The exceptional properties and characteristics of these plastics make them ideal to endure the types of pressure, stress, and damage that plastic water tanks may endure during their use.
Though polypropylene and polyethylene have similar properties, there are several versions of polyethylene that are used to produce plastic water tanks. The variations of polyethylene make it possible to adapt the plastic material to match the needs, type, and properties of plastic water tanks.
Plastic Water Tank Plastics
Polypropylene Thermoplastic
Polypropylene is a thermoplastic addition polymer made from combining propylene monomers. It was introduced in 1951 and developed quickly into a material for the production of commercial products. The major use for polypropylene is for the production of packaging materials.
As a low density plastic, polypropylene has a low weight factor that makes it attractive to manufacturers and producers. Though it has low structural use, it is ideal for the production of plastic water tanks. Polypropylene can be easily copolymerized to produce other plastics such as polyethylene.
The characteristics of polypropylene include resistance to chemicals, elasticity over a particular range, resistance to fatigue, and can be made transparent.
Polyethylene Plastics
There are five versions of polyethylene, which are polyethylene (PE), High Density Linear Polyethylene (HDLPE), Cross Linked High Density (XLPE), Ultra High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMW), and Linear Low Density (LLDPE).
Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) – LDPE has flow properties that make it ideal for manufacturing shopping bags and plastic films. It has high ductility but low tensile strength and tends to stretch when it is strained, which limits its use in the manufacture of plastic water tanks.
Linear Low-Density Polyethylene (LLDPE) – LLDPE has the same use as LDPE but with superior strength and endurance. Its toughness makes it an ideal material for storing and protecting products. Regardless of its positive properties, it has limited use in the manufacture of plastic water tanks.
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) – HDPE is the most robust and strong of the different types of polyethylene. It has a high melting point that helps in keeping it rigid in the presence of high temperatures. When it reaches its melting point, HDPE can easily be molded and shaped, which makes it ideal for manufacturing plastic water tanks. Additionally, it is resistant to mold, mildew, rotting, and harsh stressful weather conditions.
Cross Linked Polyethylene (XLPE) – XLPDE is a form of high density polyethylene with covalent bonds between the polymer chains, which are created by heat, chemicals, and radiation. The process gives the polymer chains enhanced physical properties such as stress crack resistance, toughness, stiffness, and exceptional chemical resistance. The improved properties of XLPE give plastic water tanks greater structural integrity.
Ultra High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMW) – UHMW is an extremely dense version of PE that is very strong, lightweight, and durable with strength that is superior to other plastics. It is resistant to abrasion, impact, and wear even though it is very lightweight. UHMW has a very high melting point, making it ideal for high temperature applications.
An indication of the strength of UHMW is its use as a material for the lining of bulletproof vests. The characteristics of UHMW are similar to HDPE with the addition of resistance to concentrated acids, alkalis, corrosive chemicals, and organic solvents.
Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF)
PVDF is produced by the polymerization of difluoroethylene. It has good tensile strength but has low endurance to impact. PVDF is non-flammable as well as self-extinguishing. Although not completely, it is resistant to the effect of UV light. PVDF has a very low melting point and is resistant to corrosion.
With durability against corrosion, absorption, weathering, and degradation, PVDF has a wide range of industrial uses. It can be easily shaped, manipulated, and fabricated with properties that are superior to PVC, polyethylene, and steel.
Conclusion
- A plastic water tank is a large capacity container designed to store water for household, agricultural, irrigation, and industrial manufacturing use.
- The varieties of plastic water tanks range from ones that can be carried and placed in a truck to ones that can hold thousands of gallons of water and be buried. Essentially, there is a plastic water tank for every application and function. The many types and kinds make it possible for plastic water tanks to be able to fit any purpose.
- Plastics are used for the manufacture of water tanks because of their flexibility to be produced in different sizes with a wide variety of components, additions, and types of materials to fit the type of water.
- There are an endless number of uses for plastic water tanks, aside from their basic purpose for storing water. The wide varieties of uses are due to the adaptability and flexibility of plastic water tanks, which can be configured, shaped, designed, and engineered to perform an assortment of functions.
- There are two polymers used to produce most plastic water tanks: polypropylene and polyethylene. The exceptional properties and characteristics of these plastics make them ideal to endure the types of pressure, stress, and damage that plastic water tanks may endure during their use.
